[ad_1]

Finally, the suspense is around. The James Webb House Telescope is open for science! These days, in a large joint convention with the ESA and CSA, NASA launched the initial science pictures from the entirely operational JWST. Mission experts selected these elegance photographs as an suitable showcase of Webb’s instruments and abilities.
So, without even more ado:
DEEP Subject
“Space is massive. You just will not think how vastly, hugely, intellect-bogglingly big it is. I indicate, you could consider it is a extended way down the highway to the chemist’s, but that is just peanuts to house.” –Douglas Adams, The Hitch-Hiker’s Guidebook to the Galaxy
The initial impression, an ultra-deep-area snapshot of the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723, was introduced by Jane Rigby of NASA’s Goddard Room Heart. NASA officers uncovered this incredibly 1st inaugural impression from the fully operational telescope to President Biden past night time.

In a televised briefing to President Biden, NASA officials and Webb job scientists unveiled this incredibly initially inaugural image from the James Webb place telescope.
Hunting into the deep sky signifies searching back in time. And this is a deep dive indeed. In this impression, we see the universe as it was, additional than 13 billion years in the past. Distant galaxies develop into streaks and arcs throughout the sky, distorted by gravitational lensing.
But the graphic building headlines is only half the tale. At left is what MIRI (Webb’s center-infrared digicam) sees at appropriate, NIRCam’s look at of the exact same patch of sky. Notice the vivid reds and blues in the remaining-hand picture. These celestial characteristics shine in wavelengths of gentle far too lengthy for NIRCam to see. MIRI, nevertheless, can see them just wonderful.

The galaxies in this picture seem as they were at about the same time that the Sunshine and our Earth formed. “There are galaxies right here in which we’re viewing person clusters of stars forming, popping up just like popcorn,” reported Jane Rigby in this morning’s briefing. “And in the track record, littered like jewels, are these faint red galaxies. Which is what we built the telescope to do. The most distant, we’re observing as they appeared 13 billion several years ago.”
Telescope Time
One of the major issues for the workforce was playing plan Tetris with the quite a few astronomers and scientists asking for telescope time. Ordinarily the tempo of telescope observation is rather sedate. Hubble would have taken weeks to deliver a deep-subject picture like this. But what Hubble can do in months, Webb can do in hrs. When compared to the position quo, “Webb took this picture prior to breakfast,” explained Rigby. It took just around twelve several hours to get this deep-industry portrait showing dozens of galaxies. That snappy speed implies experts can get a total good deal more finished in just their allotted time on the telescope.
Luckily, however, we mere mortals are below no this sort of time pressure. NASA has a deep-zoom characteristic, the place you can investigate this image at your leisure and commit as a great deal time as you like, zooming in and enjoying close to.
EXOPLANETS
The next impression showed the water vapor that Webb sees in the steamy environment of an exoplanet named WASP 96b.

Knicole Cólon in-depth what Webb unveiled about this nearby ‘hot Jupiter,’ possibly a thousand mild-years absent. Facts from floor-based telescopes experienced proven WASP 96b to be an unusually cloudless world. But from area, Webb was ready to discern clouds and climate styles on the planet’s surface area. Untroubled by Earth’s environment, Webb can see the planet’s surface area features with beautiful clarity.
James Webb: Open up for Science, in Residing Color
The JWST tends to make its observations in the infrared band of the EM spectrum. But because the infrared band has a more time wavelength than the seen spectrum, our eyes just can’t perceive that gentle. So how do we convert that info into some thing the human eye can see and interpret?
“We’re in essence translating light that we cannot see into light-weight that we can see, by making use of colour, like pink, environmentally friendly and blue, to the diverse filters we have from Webb,” described Webb mission scientist Joe Depasquale. “The motive we do this is that you can get more facts from the picture if you can see it in coloration.”
“We take the shortest wavelengths of infrared mild, and assign them blue hues, and then go our way down to inexperienced and red as we go to extended and extended wavelengths.”
Colorizing the photographs in this way reveals further structures that glance distinct at subtly diverse wavelengths of light-weight. Employing that more data, astronomers can make a lot more exact observations and attract superior conclusions.
“So, it is a issue of selecting and picking filters and colours that boost the information and the structure in the impression itself,” extra Webb graphic scientist Alyssa Pagan. “And then we additively incorporate those people together to get our comprehensive-shade picture.”
STELLAR Demise
3rd is a glamour shot of a dying binary star, whose dying throes established a planetary nebula called the Southern Ring. These two infrared photos show the fiery end of the star’s lifestyle.
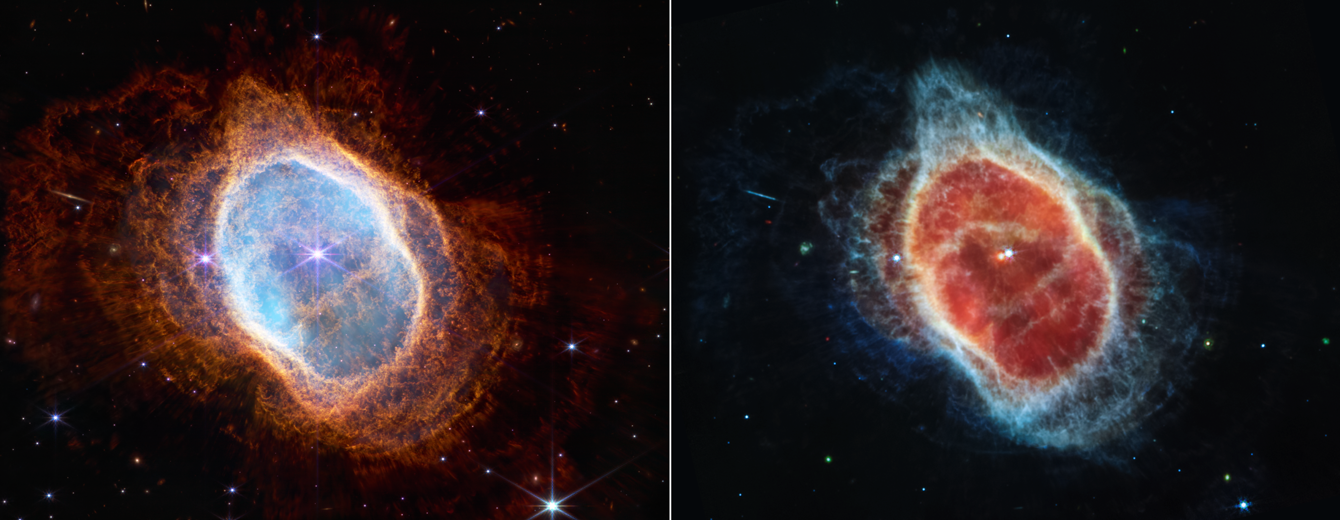

In the remaining-hand impression, captured by Webb’s close to-infrared NIRCam, you can see a great deal of framework. Initially, there’s a series of concentric shells. These shells are created by “a dying star that has dispelled a massive fraction of its mass in successive waves,” reported Webb instrument scientist Karl Gordon. Then, there’s a bubbly, “foamy” orange obvious through the nebula. The orange “foam” is molecular hydrogen, freshly established and lit from within by the nebula’s expansion.
Relocating inward, there is a blue haze at the centre of the nebula, which is ionized fuel still left over from the core of the star. It’s so incredibly hot that it is emitting “well into the blue.” An edge-on galaxy with a bright heart of mass stretches out toward the leading still left. And the rays of light seen, emanating from the center of the nebula, stand for holes or gaps in the clouds that allow the star’s light-weight to escape into room.
In the proper-hand portrait, the a person with the orange center, the orange center represents for a longer time-wavelength gentle which is shiny according to NIRCam, but dimmer to MIRI’s middle-infrared CCD. However, Gordon described, the blue is actually from molecular hydrocarbon deposits on dust grains. Then, in the centre, we can really see each stars of the binary pair.
GALAXIES
Depicted in this article is a deep-sky characteristic identified as “Stefan’s Quintet,” a intently grouped cluster of 5 galaxies. The closest galaxy in Stefan’s Quintet is the still left-most galaxy as shown in this body, and it lies about a few hundred million mild-many years from us.

This is a in the vicinity of- and mid-infrared graphic, merged. Stars in the nearest galaxy truly solve into position sources. In the other people, gas and dust form star nurseries exactly where stars are however staying born currently. Under the fiery arc, two galaxies have started merging into a single.
“If we strip absent the near-infrared check out of the stars, now in the mid-infrared with MIRI on your own, we typically see fuel and dust,” mentioned Mark McCaughrean, ESA senior advisor for Science and Exploration. “It’s the similar galaxies all over again, with the two galaxies merging. But the prime galaxy has one thing new and different in the middle of it…”

Giovanna Giardino, a Webb NIRspec expert with the ESA, defined that in the prime-most galaxy, the luminous heart is basically the infrared glow from an lively black gap. This cosmic monster outshines its host galaxy with the force of forty billion Suns. It’s invisible to the bare eye. But right here, it blazes scarlet, lit by the infrared glow of the make any difference it is devouring.
STELLAR Birth
Finally, we have this certainly breathtaking picture of the Carina Nebula. It’s a star-forming location in our personal galaxy, and it lies about 7600 gentle-yrs from Earth. Really feel absolutely free to suitable-click and open this a person whole dimension.

Amber Solid, Webb’s deputy undertaking scientist, took us on a tour of the picture. “This gorgeous vista of the ‘cosmic cliffs‘ of the Carina nebula reveals new information about this extensive stellar nursery,” mentioned Robust. “Today, for the to start with time, we’re viewing model-new stars that were being earlier fully concealed from our look at.”
Powerful defined that the graphic exhibits “bubbles and cavities, and jets that are staying blown out by these newborn stars. We even see some galaxies lurking in the history. We see structures that we do not even know what they are!”
The image is a snapshot of a dynamic, ongoing procedure. Observe the brilliant stars close to the prime of the frame. (You can pick them out by their 6-pointed halo, an artifact of Webb’s hexagonal mirrors.) The radiation and stellar wind from these gigantic, hot younger stars are blowing a cosmic bubble, urgent versus the gas and dust below.
Gasoline and dust make excellent raw materials for newborn stars in stellar nurseries. But the exact forces blowing the bubble can blow absent the fuel and dust in their turbulent wake. It’s a delicate balance, Robust included, where by new stars are forming, but the level of stellar formation is in decrease.
Upcoming Techniques
So, what arrives future for Webb? The telescope’s schedule is unquestionably booked for the subsequent comprehensive 12 months. One particular important activity for the telescope is investigating the “cosmic ladder,” which we use to figure out distances in the deep sky. Webb will be carefully observing Cepheid variable stars, AGNs, and other celestial options, to make the cosmic distance ladder more accurate.
If you’re asking yourself when we’ll lastly position the JWST at a concentrate on within the photo voltaic program, you’re in luck — we currently have! There is a huge facts launch coming Thursday, which will incorporate one thing like forty terabytes of images and raw info from Webb’s observations to day. In that data launch, we’ll discover visuals of Jupiter, alongside with other targets within our possess star program.
Now that James Webb is open up for science, astronomers will be pointing it at targets fantastic and smaller. “One of Webb’s employment is to locate out about galaxies and enable us to recognize how they adjust,” reported Katy Haswell, a Webb task scientist with the ESA. And as these photographs and many others arrive to us, we’ll be combing via them, to bring you the very greatest.
Now Browse:
[ad_2]
Resource url